CpG oligodeoxynucleotide (CpG ODN) refers to a short strand of DNA containing an unmethylated cytosine-phosphate-guanine (CpG) dinucleotide motif. In vertebrates, CpG motifs are commonly methylated and suppressed by the immune system. However, bacterial and viral DNA contains frequent unmethylated CpG motifs that are recognized as a pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP) by the innate immune system. The discovery of immune stimulatory CpG ODN in late 1990s revolutionized our understanding of innate immune mechanisms and paved way for novel vaccine adjuvants and immunotherapies.
Toll-Like Receptor 9 Signaling
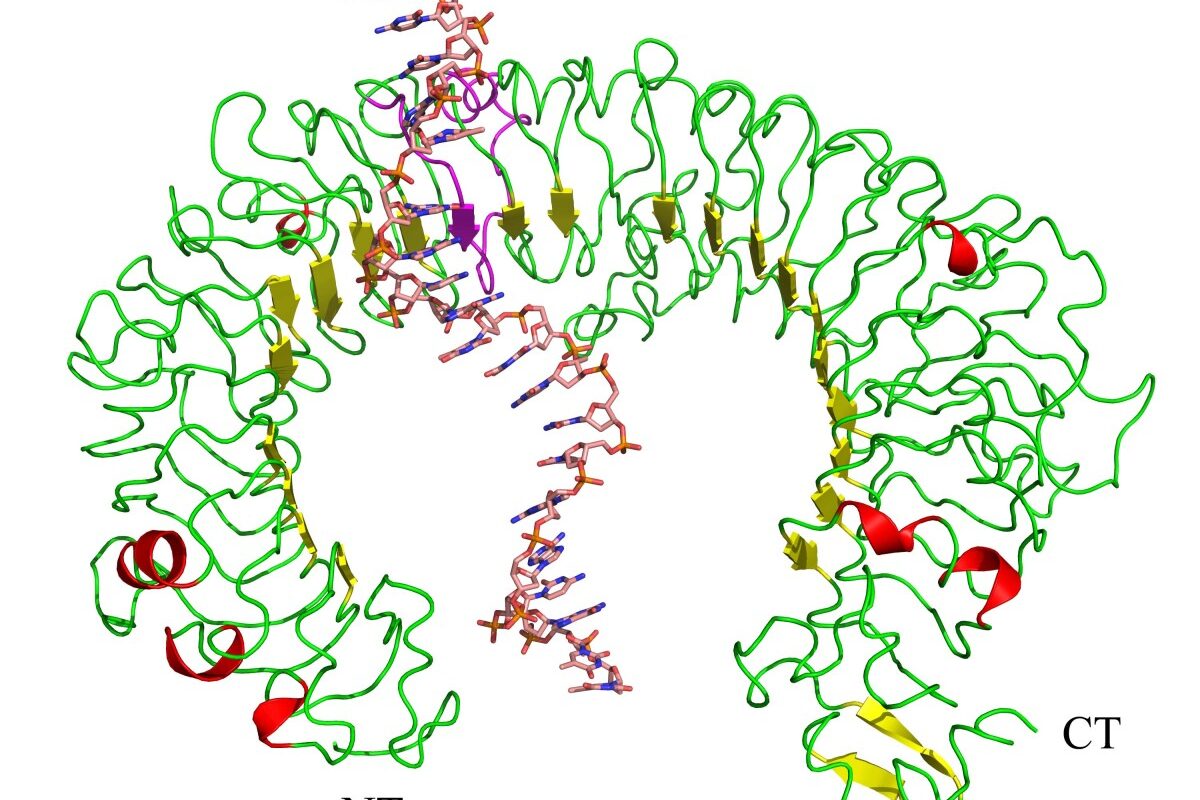
Studies in late 1990s revealed that unmethylated CpG ODN interact with endosomal Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) to induce immune activation. TLR9 is expressed predominantly by B cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs). Binding of CpG ODN to TLR9 leads to its dimerization and recruitment of myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 (MyD88). The MyD88 signaling cascade ultimately activates nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) such as p38, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). This leads to production of proinflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-6 and type I interferons (IFN-α/β). CpG ODN also causes maturation and activation of antigen presenting cells resulting in enhanced adaptive immune responses.
Sequence Motifs and Development of Class A-D CpG ODNs
Early studies found that immune effects of CpG Oligodeoxynucleotide vary with flanking nucleotide sequences. Based on sequence and immune activity, four major classes of CpG ODNs were described – class A, B, C and D. Class A CpG ODNs contain phosphorothioated CpG flanked by two 5’ purines and two 3’ pyrimidines (like 5’-purine-purine-CpG-pyrimidine-pyrimidine-3’). They strongly induce IFN-α production by pDCs through TLR9. Class B CpG ODNs stimulate both B cells and pDCs due to presence of CG dinucleotide flanked by two 5’ purines on both sides. Class C CpG ODNs contain phosphorothioated CpG in palindromic sequences and stimulate B cells. Class D CpG ODNs have non-B cell stimulatory sequences and induce IFN-α and proinflammatory cytokine production. This classification helped development of ODN sequences tailored for specific applications.
Application as Vaccine Adjuvants
Due to potent immunostimulatory properties, class A and B CpG ODNs found widespread application as vaccine adjuvants to improve vaccine immunogenicity and efficacy against infectious pathogens as well as cancer cells. Preclinical studies showed that addition of CpG ODN to subunit vaccines enhances antigen-specific antibody and T cell responses. In early human trials, CpG ODN adjuvanted vaccines against hepatitis B, influenza and other pathogens induced strong humoral and cellular immunity. Ongoing trials are evaluating the adjuvant effect of CpG ODNs for subunit vaccines against HIV, tuberculosis and cancers. CpG ODN adjuvants hold promise as alternative to alum salts commonly used in licensed vaccines.
CpG ODN in Non-Vaccine Therapeutics
Apart from vaccines, immunotherapeutic applications of CpG ODNs are being explored for cancer, allergy and infectious diseases. In cancer immunotherapy, CpG ODN is used to mature dendritic cells ex vivo before reinfusing with the patient to induce antigen-specific anti-tumor responses. Preclinical studies showed CpG ODN can activate innate immune cells to inhibit tumor growth and mediate tumor regression either alone or in combination with other agents. Several clinical trials have evaluated class A and B CpG ODNs as therapy for hematological and solid tumors. For allergic diseases, CpG ODN suppresses IgE production and skews adaptive immunity toward Th1 type. In preclinical asthma models, CpG ODN reversed established airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness. Few human trials are ongoing CpG ODN therapy for allergic rhinitis and asthma. Some studies also reported beneficial effects of CpG ODN against infectious pathogens like HIV, HCV, HBV etc.
Safety and Future Prospects
Regarding safety, majority of preclinical and clinical studies with CpG ODNs demonstrated a good toxicity profile. Most common adverse effects reported were mild to moderate flulike symptoms which subsided within few days. However, issues remain regarding oligonucleotide stability, pharmacokinetics and delivery methods. With advancement in nucleic acid chemistry and delivery systems, long acting and targeted CpG ODNs can be developed. Further clinical evaluation in larger cohorts is warranted to establish optimal dosage and regimens. Besides current applications as vaccine adjuvant and monotherapy, combination of CpG ODN with other immunomodulators holds promise. Overall, CpG ODN is an exciting immunotherapeutic platform with potential to combat cancers, chronic infections and allergic diseases.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it