Tech giants are working on developing chipless RFID tags which could revolutionize inventory management and supply chain tracking. Chipless RFID has the potential to become the next big thing in radio frequency identification, offering a cheaper and more scalable alternative to traditional RFID tags.
What is Chipless RFID?
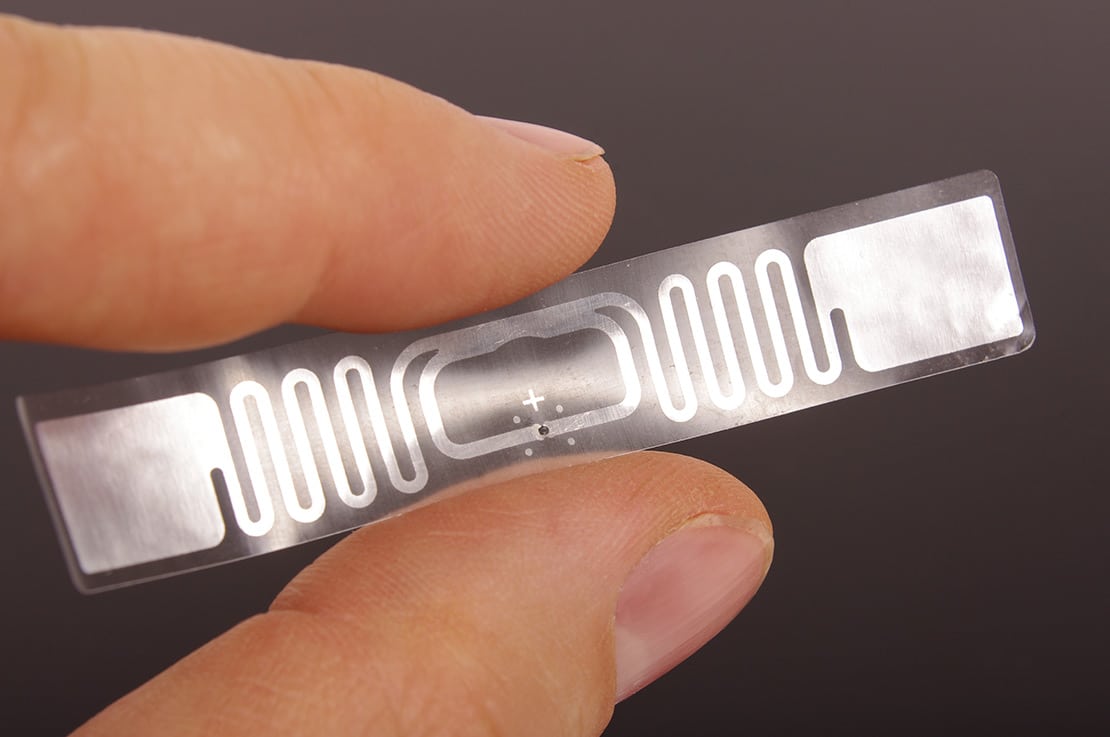
Chipless RFID or chipless radio-frequency identification utilizes radio frequency signals for identification without the need for an integrated circuit chip. In traditional RFID systems, each tag contains a silicon chip and antenna, which adds to the cost. Chipless RFID tags are simply patterns etched, printed or imprinted directly on materials like paper, cardboard, plastic or textiles. These tags backscatter the radio signals from readers to encode identifiers instead of using integrated chips. Essentially, the tags are encoded through small notches, slits or other physical irregularities that alter the tags’ electromagnetic response to interrogating radio waves.
Advantages of Chipless RFID
– No ICs required: The absence of integrated circuits makes chipless RFID tags truly zero-cost. This is a major advantage over traditional RFID tags which have integrated circuit chips.
– Extremely low-cost: Chipless RFID tags can be mass produced for mere cents or fractions of a cent each, driving their costs far lower than chip-based RFID tags. Printing techniques like gravure allow for high-volume, low-cost chipless tag manufacturing.
– Higher data capacity: While chip-based RFID tags are limited to just 128-bits or 256-bits of data storage, chipless RFID can encode several kilobits of data due to the unique nature of their electromagnetic backscattering.
– Environmentally friendly: Chipless tags are completely printable and lack inorganic material, making them more eco-friendly and biodegradable than silicon chip-based tags.
Challenges of Chipless RFID
However, chipless RFID technology is not without its technical challenges. Key issues include:
– Longer read ranges needed: Chipless tags currently have read ranges of around 3-5 meters while active RFID tags have read ranges up to 100 meters. Research is being conducted to improve chipless tags’ read ranges.
– Complex encoding and decoding: Chipless tags encode data through complex electromagnetic signatures which require sophisticated algorithms to decode. Existing systems can only handle low data rates.
– Interference issues: Deploying a large number of chipless tags in proximity may cause signal interference due to tag-to-tag near-field couplings.
– Standardization needed: For chipless RFID to scale, common standards need to be established around tag encoding, energy harvesting mechanisms, and authentication protocols.
Applications and Market Potential
Despite existing challenges, chipless RFID holds immense promise in supply chain and logistics applications due to its ultra-low costs. Key sectors that could integrate chipless RFID include:
– Item-level apparel tagging: Clothing retailers are testing woven chipless RFID tags in garment labels and care tags for real-time inventory tracking.
– Item-level food tracking: Per item encoding of meat, fish and produce allows monitoring freshness and prevents contamination across the cold food supply chain.
– Pharmaceutical Serialization: Serialization of drug packages can significantly curb counterfeiting with high-data-capacity chipless RFID.
– Logistics asset tracking: Pallets, boxes, containers and returnable transport items can be easily marked and tracked globally using chipless RFID stickers.
It is estimated chipless RFID market could reach $5 billion by 2030 as deployment scales up. Major tech firms like Microsoft and MIT are dedicating R&D resources towards solving technical bottlenecks, evangelizing global standards and accelerating the technology’s commercialization. If challenges around higher read ranges and complex encoding/decoding can be overcome, chipless RFID has the ability to truly revolutionize digital identification and transform supply chain efficiency across industries worldwide.
*Note:
- Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
- We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it