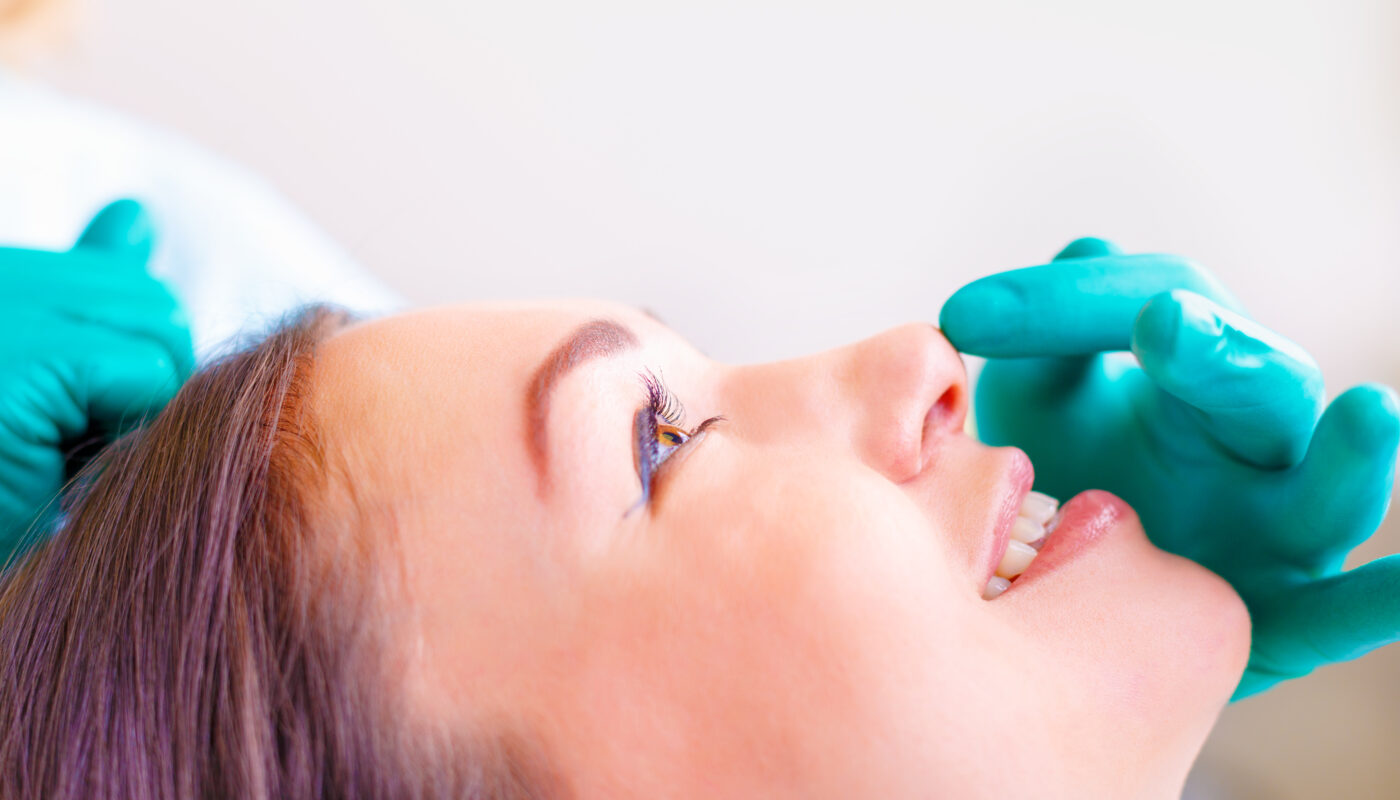
Rhinoplasty, also known as nose surgery, is a cosmetic surgical procedure that reshapes and restructures the nose to improve its appearance, symmetry and proportion. It is one of the most commonly performed cosmetic surgeries today. Rhinoplasty is performed to change the size, shape or angle of the nose or to fix nasal problems like a deviated septum. Through careful restructuring of the nose, the surgeon aims to create a nose that is in harmony with the individual’s facial features.
Reasons to Consider Rhinoplasty
There can be several reasons why someone may consider Rhinoplasty. Some common reasons include:
Improving the Nose Aesthetics
Many patients seek rhinoplasty to enhance their overall facial appearance and self-esteem by fixing perceived imperfections in the nose like a hump, crookedness or width. It helps achieve a nose they feel fits their face better.
Correcting Breathing Problems
For some, Rhinoplasty is performed to correct structural issues that disrupt normal breathing or airflow such as a deviated septum. Improving nasal breathing can boost quality of life.
Accident or Injury Repair
Rhinoplasty may also be necessary after physical trauma to realign and rebuild a broken or damaged nose following injuries from accidents, nasal fractures or previous surgeries.
Types of Rhinoplasty Procedures
Depending on the goals and extent of correction needed, rhinoplasty can be classified as either cosmetic or functional. There are two main types of nose surgery procedures:
Closed Rhinoplasty
In the closed technique, incisions are made inside the nose so there are no external scars. It is best option for minor or subtle reshaping of the nasal structure.
Open Rhinoplasty
An open rhinoplasty involves an additional incision across the columella (the skin between nostrils) so cartilage and bone inside can be accessed directly. This technique provides better visualization and control for complex reshaping needs or reconstructive cases.
The Rhinoplasty Process
Here are the standard steps involved in the rhinoplasty procedure:
Consultation: An in-depth consultation with a board-certified facial plastic surgeon is done to understand goals, concerns and do necessary evaluations before any treatment plan.
Anesthesia: Rhinoplasty is performed under general anesthesia to ensure patient comfort and safety during surgery that typically takes 1-3 hours.
Incisions: Based on technique (open or closed), incisions are made inside or both inside and outside nose for access to underlying structures.
Modification of Bones and Cartilage: The nasal bones and cartilage are sculpted or resected as needed to achieve desired shape through techniques like osteotomies or caudal extension.
Augmentation and Grafting: Broken or missing nasal bones, cartilage may be supported or reconstructed using medical implants and grafts.
Setting and Alignment: The corrected nasal framework is precisely set into correct alignment and position for balanced aesthetics.
Closure: Incisions are closed with fine sutures or surgical tapes internally and externally depending on technique used. Nasal splint or pack supports heal properly.
Recovery from Rhinoplasty
Recovery after rhinoplasty takes 1-4 weeks. Some common aftercare involves:
Use of splint, tapes, packing for initial support and healing
Application of ice packs for swelling and bruising
Head elevation and limited physical activity
Nasal saline sprays for moisture and cleaning
Antibiotics to prevent infection
Managing pain and discomfort with prescription medications
Follow up visits assess healing progress
It takes around 6-12 months for final results to stabilize as swelling fully resolves. Minor tweaking can sometimes be done to refine outcomes. However, rhinoplasty is considered a permanent change that greatly enhances facial appearance and confidence. With a skilled surgeon, it is a safe and effective procedure to obtain the nose shape one has always wanted.
Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research.
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it.