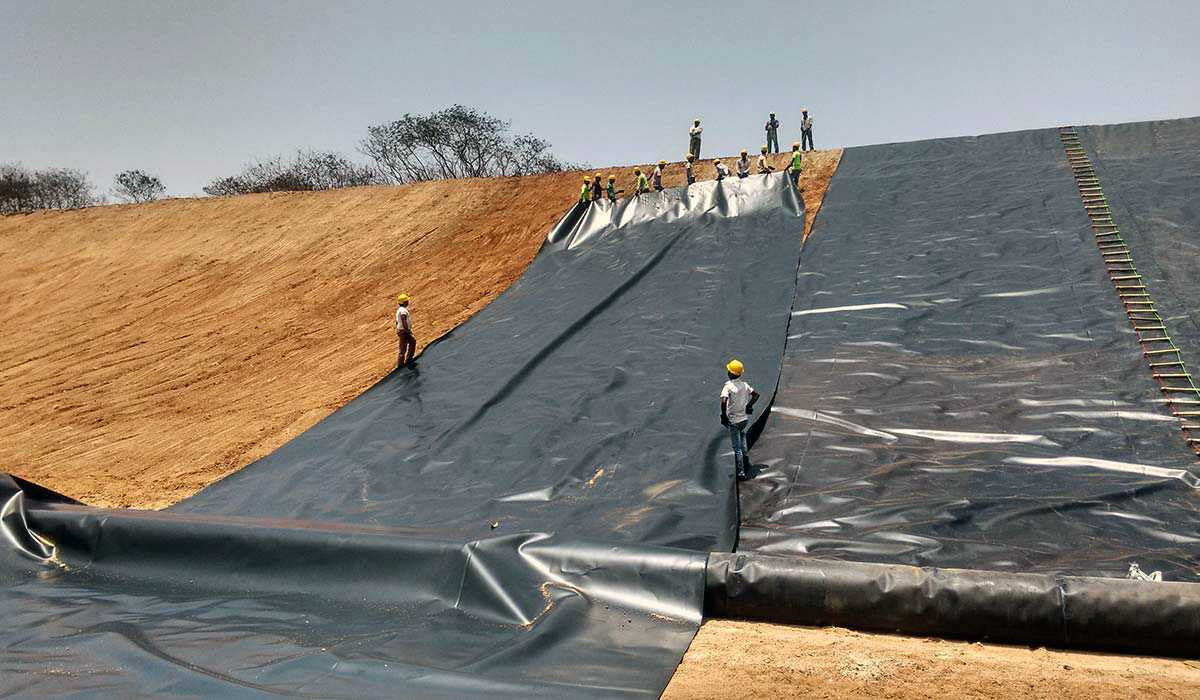
Geomembranes are impermeable synthetic membrane liners that are used in civil engineering projects for applications like landfills, mining waste containment, and reservoir lining. They are manufactured from polymers like HDPE (high-density polyethylene), LLDPE (linear low-density polyethylene), PVC (polyvinyl chloride), and HDPE/LLDPE geocomposites and are designed to be essentially impermeable to fluid migration for long-term performance. The key advantages of geosynthetic include flexibility, chemical resistance, longevity, low permeability, and relative ease of installation.
Types
There are different types of geosynthetic available based on the polymer used in their manufacture:
– HDPE Geosynthetic: Made from HDPE, these are the most commonly used geosynthetic. HDPE has good chemical resistance and flexibility at low temperatures. HDPE geosynthetic have very low permeability.
– LLDPE Geosynthetic: Manufactured using LLDPE, these geosynthetic have similar properties to HDPE but are more flexible at lower temperatures.
– PVC Geosynthetic: Made from PVC, these geosynthetic have very low permeability and good resistance to oxidizing chemicals. However, they have less flexibility compared to HDPE/LLDPE.
– HDPE/LLDPE Composite Geosynthetic: These geosynthetic consist of an HDPE or LLDPE film laminated or extruded with a nonwoven geotextile for added puncture and tear resistance.
Geosynthetic Manufacturing Methods
The key manufacturing methods used for producing geosynthetic are:
– Extrusion: The polymer is melted and extruded through a die to form long sheets which are then rolled. This is the most common method.
– Calendering: The polymer resin is heated, pressed, and passed through rollers to obtain the desired thickness. Useful for textured geosynthetic.
– Chemical Bonding: The resin is applied to a geotextile substrate via a chemical bonding process to produce geosynthetic composites.
Quality Assurance Testing of Geomembranes
Extensive quality control testing is conducted on geosynthetic to ensure they meet the required standards for long-term performance in challenging site conditions:
– Thickness Measurement: Geomembranes Ultrasonic gauges measure geosynthetic thickness at regular intervals to ensure uniformity.
– Tensile Properties Testing: Tests the geosynthetic’s strength, elongation, and tear resistance as per ASTM standards.
– Hydrostatic Resistance Testing: Measures the material’s ability to resist hydraulic pressures via tests like the Burst Test.
– Penetration Resistance Testing: Ensures the material can withstand punctures from sharp objects like stones.
– Seam Testing: Destructive and non-destructive tests are conducted on field seams to check for continuity and defects.
Applications of Geomembranes in Waste Management
Some key applications of geosynthetic in waste containment and management include:
– Landfill Liners: Geosynthetic form the primary or secondary liner at municipal and hazardous waste landfills to prevent leachate seepage into soils and groundwater.
– Mining Waste Containment: Used for lining mine tailings impoundments and heap leach pads to contain process chemicals and wastewater from oxidation.
– Agricultural Waste Lagoons: Geomembranes Geosynthetic are used to line anaerobic lagoons and waste storage ponds at industrial livestock/dairy farms.
– Wastewater Treatment & Storage: Commonly used for lining oxidation ponds, percolation ponds, equalization basins, and sludge storage areas at wastewater treatment plants.
– Reservoir Lining: Provides an impermeable layer at potable water reservoirs and water storage tanks to prevent contamination of stored water.
Benefits of Geosynthetic Over Compacted Clay Liners
While compacted clay liners (CCLs) were traditionally used, geosynthetic provide several benefits:
– High Permeability: Geosynthetic are many orders of magnitude less permeable than even the best CCLs, ensuring decades of containment reliability.
– Consistency: Geosynthetic quality is uniform throughout, unlike CCLs which can have defects due to compaction variability.
– Longevity: Properly installed geosynthetic have a design service life of 50-100 years with no maintenance required.
– Speed: Geosynthetic can be installed much faster and with fewer mobilizations compared to CCL construction.
– Cost Savings: Though higher capital cost initially, geosynthetic provide significant operational cost savings over the long-term versus CCLs.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it