Central fill pharmacies utilize automated systems and processes to consolidate prescription filling operations into a centralized facility separate from the retail pharmacy location. This centralized model allows multiple retail pharmacies to leverage the efficiencies of high-volume prescription processing in one location. By consolidating filling operations, central fill pharmacies are able to standardize workflows, deploy advanced automation technologies, and allocate personnel more optimally compared to traditional pharmacy settings.
How Central Fill Pharmacies Work
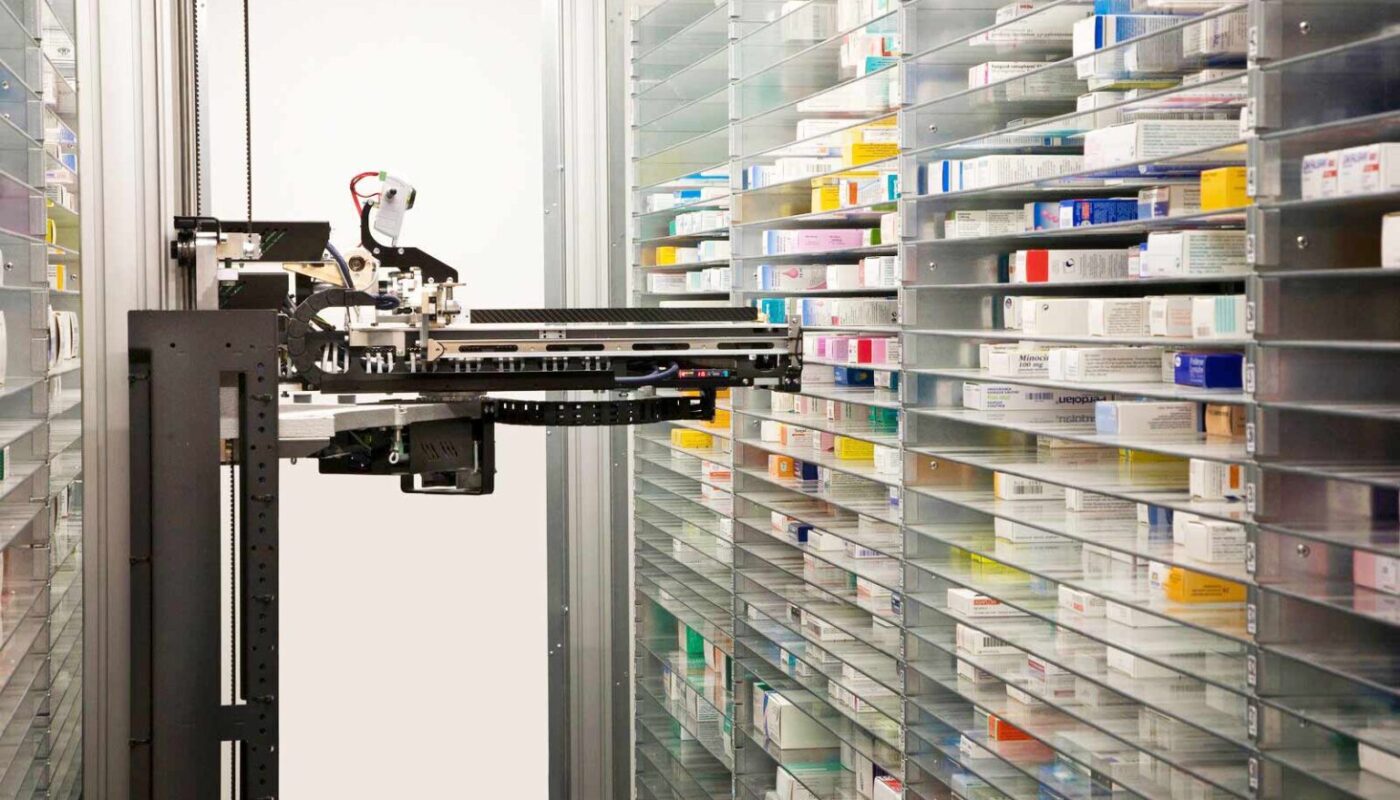
In a Central Fill Pharmacy Automation, new prescriptions are sent electronically from multiple retail locations to the central fill site for processing. Trained technicians at the central fill facility then utilize automated medication dispensing and packaging systems to accurately fill prescriptions at high volumes. Once filled, the prescriptions are quality-checked and then shipped or delivered back to the originating retail pharmacy for pickup by the patient. This centralized approach separates the prescription intake, counselling and customer service aspects handled at each retail store from the back-end fulfilling operations centralized at one high-capacity site.
Benefits of Automation in Central Fill Pharmacies
Central fill pharmacies are designed around optimizing the advantages that automation provides. Advanced medication dispensing robots, verification technologies and packaging systems allow a small team of technicians to accurately process thousands of prescriptions per day, far exceeding what could be safely achieved manually. Key benefits of automation in central fill settings include:
Increased Accuracy: Automated systems such as counting robots, visual inspection tools and barcode scanning drastically reduce human error potential compared to manual filling. This enhances patient safety.
Higher Productivity: Robotic arms, carousels and automated packaging lines enable a single technician to process 2-3 times as many prescriptions per hour as traditional manual methods.
Standardization: Automation promotes consistent, error-proof workflows that are less prone to variances between individual pharmacy staff. This leads to more uniform quality across locations.
Scalability: Central fill pharmacies can readily increase capacity and throughput by adding more automated cells or lines as prescription volumes grow, unlike relying solely on hiring and training additional human staff.
Staff Optimization: Automation handles the physically demanding tasks of counting, picking and packaging medications, allowing technicians to focus on higher-level activities like verification, problem-solving and quality control. This creates a more ergonomic, less strenuous work environment.
Types of Automated Systems Used
State-of-the-art central fill pharmacies utilize a variety of specialized automation solutions tailored for high-volume prescription processing:
Automated Dispensing Cabinets: Vast robotic cabinets with thousands of medication bins use barcode scanning to rapidly retrieve and confirm the accuracy of individual doses for filling.
Robotics Workcells: Multi-armed industrial robots dexterously pick, count, and organize medications for filling at lightning speeds far exceeding humans.
Vial/Blister Packaging Machines: High-speed automated lines produce precisely sealed multi-dose medication cards and bottles with customizable labelling.
Verification Technologies: 3D scanning, weight checking and other mechanisms double-check each step of the filling process to ensure the highest levels of accuracy.
Conveying and Sorting Systems: Automated carousels, chutes and sorting stations efficiently route prescriptions between technician work areas and integration points with other systems.
The implementation of these types of integrated automation solutions is revolutionizing the capabilities and productivity of high-volume central fill pharmacies.
Continuous Process Improvements
Given the fast pace of technological innovation, leading central fill pharmacies take a continuous improvement mindset towards identifying new ways to optimize automation over time. As newer, more advanced systems emerge, pharmacies routinely evaluate opportunities for:
expanding automation to take over additional manual functions to further reduce human intervention points and chances for error.
Increasing system throughput to accommodate rising prescription demand volumes and same-day fulfillment expectations.
maximizing space utilization through more compact footprint equipment and optimized material flows between functions.
-Leveraging predictive analytics of historical dispensing patterns to better pre-stage and sequence prescriptions in automated systems.
-Implementing new technologies like robotic vision systems, artificial intelligence, and augmented reality to further enhance precision, scalability, and consistency of filling operations.
This constant refining of automated workflows and processes is key to maintaining quality and productivity leadership as central fill pharmacy capabilities continue to advance rapidly.
Central fill pharmacies represent a major transformation towards optimizing prescription fulfillment through automation, standardization, and consolidation of operations. Leveraging advanced robotic, verification, and packaging solutions integrated within well-designed facilities, central fill allows for unparalleled accuracy, throughput, and staff productivity that would otherwise be impossible in traditional pharmacy settings. As these automated models continue to advance, central fill is poised to play an increasingly vital role in meeting the ever-growing demand for prescription medications across various healthcare settings.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it